3. Introduction to Types of SEO: On-Page, Off-Page, and Technical SEO
Introduction to Types of SEO: On-Page, Off-Page, and Technical SEO
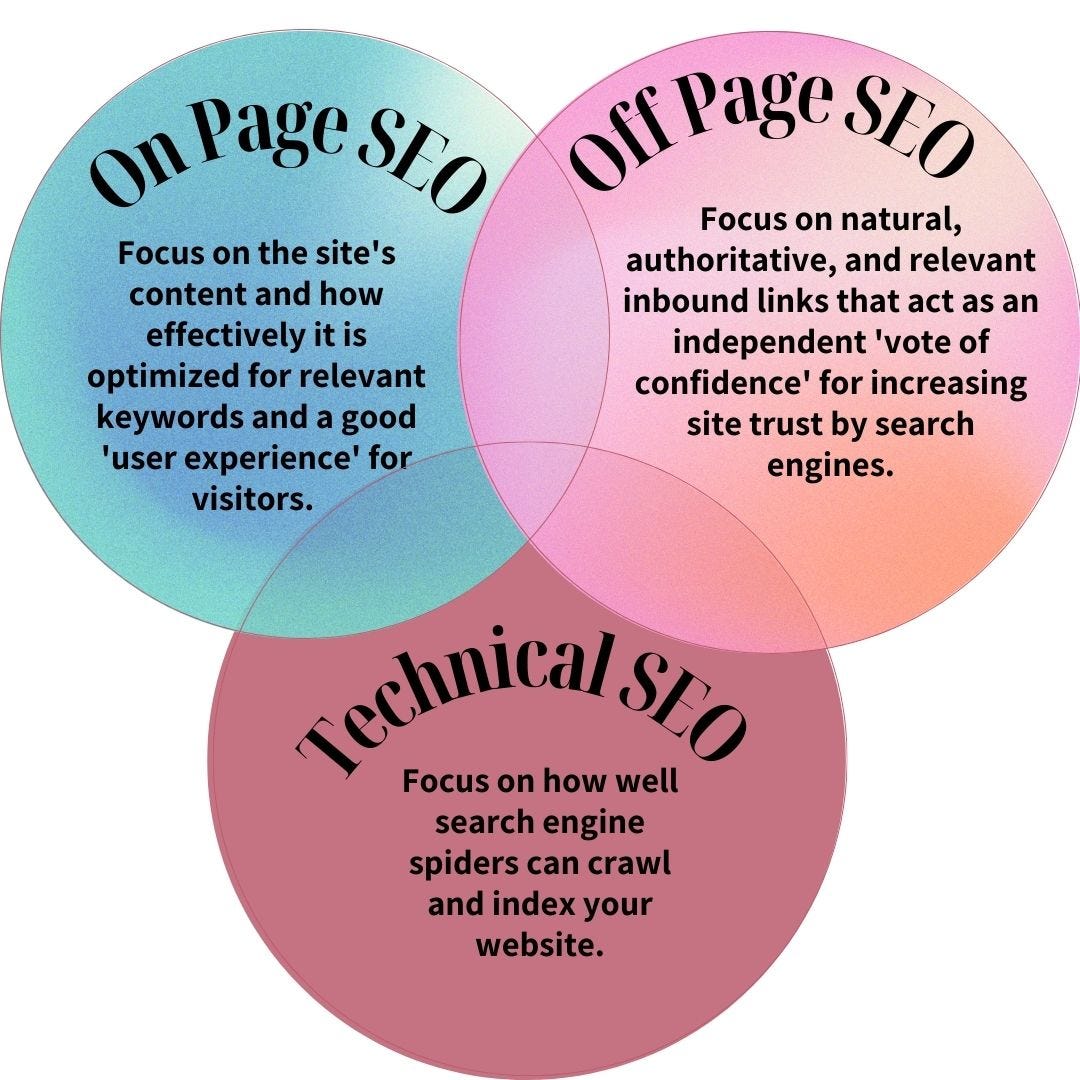
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is essential for any website aiming to improve its visibility on search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo. SEO isn’t a one-size-fits-all approach; it’s a multi-faceted strategy involving several different types, each with its unique focus and purpose. To effectively optimize your website, it’s crucial to understand the three primary types of SEO: On-page SEO, Off-page SEO, and Technical SEO.
1. What is SEO and Why Is It Important?
SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is the practice of optimizing your website to rank higher on search engine results pages (SERPs). Higher rankings lead to increased organic traffic, which means more potential customers or users for your website. SEO is vital because:
- Increases Visibility: The higher you rank on SERPs, the more likely users will visit your website.
- Builds Credibility and Trust: High-ranking websites are often perceived as more authoritative and trustworthy.
- Improves User Experience: Many SEO practices, such as improving site speed and mobile usability, enhance the overall user experience.
- Offers Long-term Benefits: Unlike paid ads, SEO efforts provide sustainable results over time, generating consistent traffic without ongoing costs.
Now, let’s explore the different types of SEO that collectively contribute to a successful strategy.
2. On-Page SEO: Optimizing Content and HTML
On-Page SEO refers to the process of optimizing individual web pages to improve their search engine rankings and attract more relevant traffic. It focuses on both the content and HTML source code of a page, ensuring that it aligns with the search engine’s ranking factors. Key components of On-Page SEO include:
a. Keyword Research and Optimization
Keyword research is the foundation of On-Page SEO. It involves identifying the terms and phrases your target audience is likely to use when searching for information related to your content. Once you have a list of relevant keywords, the next step is keyword optimization:
- Title Tags: The title tag is one of the most critical elements for On-Page SEO. It should contain the primary keyword and be compelling enough to attract clicks.
- Meta Descriptions: This brief summary of the page content should include the main keyword and entice users to click through from the SERPs.
- Headers (H1, H2, H3, etc.): Use headers to structure your content logically. Include relevant keywords in H1, H2, and other headers to help search engines understand the page’s hierarchy and content.
- Content Quality and Relevance: Create high-quality, informative, and engaging content that addresses the user’s intent. Content should be unique, well-written, and provide real value to your audience.
b. Content Optimization
Content is the backbone of On-Page SEO. Search engines aim to deliver the most relevant and valuable content to users, so optimizing your content is key:
- Use Natural Language and LSI Keywords: Avoid keyword stuffing. Instead, use related keywords (Latent Semantic Indexing or LSI keywords) to provide context and make the content flow naturally.
- Multimedia Elements: Incorporate images, videos, infographics, and other multimedia elements to enhance user engagement. Ensure all multimedia elements have optimized alt tags and descriptions.
- Internal Linking: Use internal links to guide users to related content within your website. This helps to reduce bounce rates and distribute link equity across your pages.
- Readability and Formatting: Ensure your content is easy to read and scan by using bullet points, short paragraphs, and clear headings.
c. Image Optimization
Images are crucial for enhancing the visual appeal of your content, but they also play a significant role in SEO:
- File Names: Use descriptive, keyword-rich file names for your images.
- Alt Text: Add alternative text (alt text) to describe what the image represents. This helps search engines understand the context and improves accessibility for visually impaired users.
- Compression: Optimize image sizes to improve page load speed, which is a critical ranking factor.
d. URL Structure
An SEO-friendly URL structure helps search engines understand the content of your pages:
- Keep URLs Short and Descriptive: Include primary keywords in the URL and keep them concise.
- Use Hyphens to Separate Words: Use hyphens (-) instead of underscores (_) to separate words in URLs.
3. Off-Page SEO: Building Authority and Trust
Off-Page SEO refers to all activities outside your website that impact its authority, trustworthiness, and relevance. The primary goal of Off-Page SEO is to build your website’s reputation through external signals, such as backlinks, social media mentions, and other online references.
a. Backlinks: The Backbone of Off-Page SEO
Backlinks, also known as inbound or incoming links, are one of the most critical components of Off-Page SEO. They serve as endorsements from other websites, signaling to search engines that your content is valuable and trustworthy.
- Quality Over Quantity: Focus on obtaining backlinks from reputable and high-authority websites in your industry. A few high-quality backlinks are more valuable than numerous low-quality ones.
- Diverse Backlink Profile: Aim for a mix of backlinks from various domains, such as blogs, news sites, directories, and forums. This diversity enhances your website’s authority.
- Anchor Text Optimization: Use relevant and natural anchor text for backlinks. Avoid over-optimization, as it can lead to penalties.
b. Social Signals
Social media platforms play an important role in Off-Page SEO by driving traffic and engagement to your website:
- Content Sharing: Encourage users to share your content on social media to increase visibility and generate backlinks.
- Brand Mentions: Engage with your audience on social media to increase brand awareness and create positive mentions that build trust.
- Influencer Outreach: Collaborate with influencers in your niche to expand your reach and acquire quality backlinks.
c. Guest Blogging
Guest blogging is an effective way to build backlinks and establish your authority in your industry:
- Write High-Quality Guest Posts: Contribute valuable content to reputable websites in your niche.
- Link Back to Your Website: Include relevant backlinks to your website within the content or author bio.
- Build Relationships: Use guest blogging opportunities to build relationships with other industry experts and website owners.
d. Online Reputation Management
Maintaining a positive online reputation is crucial for Off-Page SEO:
- Monitor Brand Mentions: Use tools to track mentions of your brand online and respond promptly to both positive and negative feedback.
- Encourage Positive Reviews: Ask satisfied customers to leave positive reviews on platforms like Google My Business, Yelp, and Trustpilot.
- Engage with Your Audience: Respond to comments, questions, and feedback on your website, social media, and third-party platforms.
4. Technical SEO: Enhancing Crawlability and Performance
Technical SEO involves optimizing the technical aspects of your website to ensure search engines can crawl, index, and rank your content effectively. While On-Page and Off-Page SEO focus on content and external factors, Technical SEO focuses on the backend structure and performance of your site.
a. Website Speed Optimization
Site speed is a critical ranking factor and plays a significant role in user experience:
- Minimize HTTP Requests: Reduce the number of requests made by your site to load all resources, such as images, scripts, and stylesheets.
- Use Browser Caching: Enable browser caching to store frequently accessed files, reducing load times for returning visitors.
- Optimize Images and Videos: Compress images and videos without losing quality to reduce loading times.
b. Mobile-Friendliness
With the increasing number of mobile users, optimizing your site for mobile devices is crucial:
- Responsive Design: Ensure your website is responsive, meaning it adapts to different screen sizes and devices.
- Mobile Usability: Test your website’s mobile usability to ensure elements like buttons, fonts, and forms are easy to use on mobile devices.
c. Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
Security is an important factor for both search engines and users:
- Use HTTPS: Ensure your website is secured with HTTPS, which encrypts data between the user and the server. Websites with HTTPS are prioritized by search engines and provide a sense of trust to users.
d. XML Sitemap and Robots.txt
Help search engines crawl and index your website effectively:
- XML Sitemap: Create and submit an XML sitemap to search engines to provide a clear map of all your website’s pages.
- Robots.txt File: Use the
robots.txtfile to instruct search engines on which pages they should or shouldn’t crawl.
e. Structured Data and Schema Markup
Use structured data and schema markup to help search engines understand your content:
- Rich Snippets: Use schema markup to provide additional information in search results, such as product reviews, event dates, and recipes.
- Knowledge Graph: Help your content appear in Google’s Knowledge Graph by using structured data to provide detailed information.
5. How to Implement a Holistic SEO Strategy
To create a successful SEO strategy, you need to combine all three types of SEO: On-Page, Off-Page, and Technical. Here’s how:
- Start with a Strong Foundation: Begin with Technical SEO to ensure your website is crawlable, fast, and secure.
- Focus on Quality Content: Develop high-quality, keyword-optimized content that addresses user intent and provides value.
- Build Authority and Trust: Use Off-Page SEO tactics like backlink building, social media engagement, and reputation management to establish authority in your niche.
- Monitor and Adapt: Regularly analyze your SEO performance using tools like Google Analytics and Search Console. Adjust your strategy based on
Read more: